Urine tests are among the most common diagnostic tools used to assess overall health, especially kidney and urinary tract function. One of the key parameters doctors look for in a routine urine examination is the presence of pus cells. Many people become concerned when they see pus cells mentioned in their report and immediately search for the pus cells in urine normal range to understand whether their results are alarming or not.
This detailed guide explains what pus cells are, the pus cells in urine normal range, why they appear in urine, associated symptoms, possible causes, and when medical attention is required.
What Are Pus Cells in Urine?
Pus cells are white blood cells (WBCs) that help the body fight infections. When pus cells appear in urine, the condition is known as pyuria. These cells usually enter the urine when there is inflammation or infection in the urinary tract, kidneys, bladder, or urethra.
Checking the pus cells in urine normal range helps doctors determine whether the urinary system is functioning normally or if there is an underlying problem that needs attention.
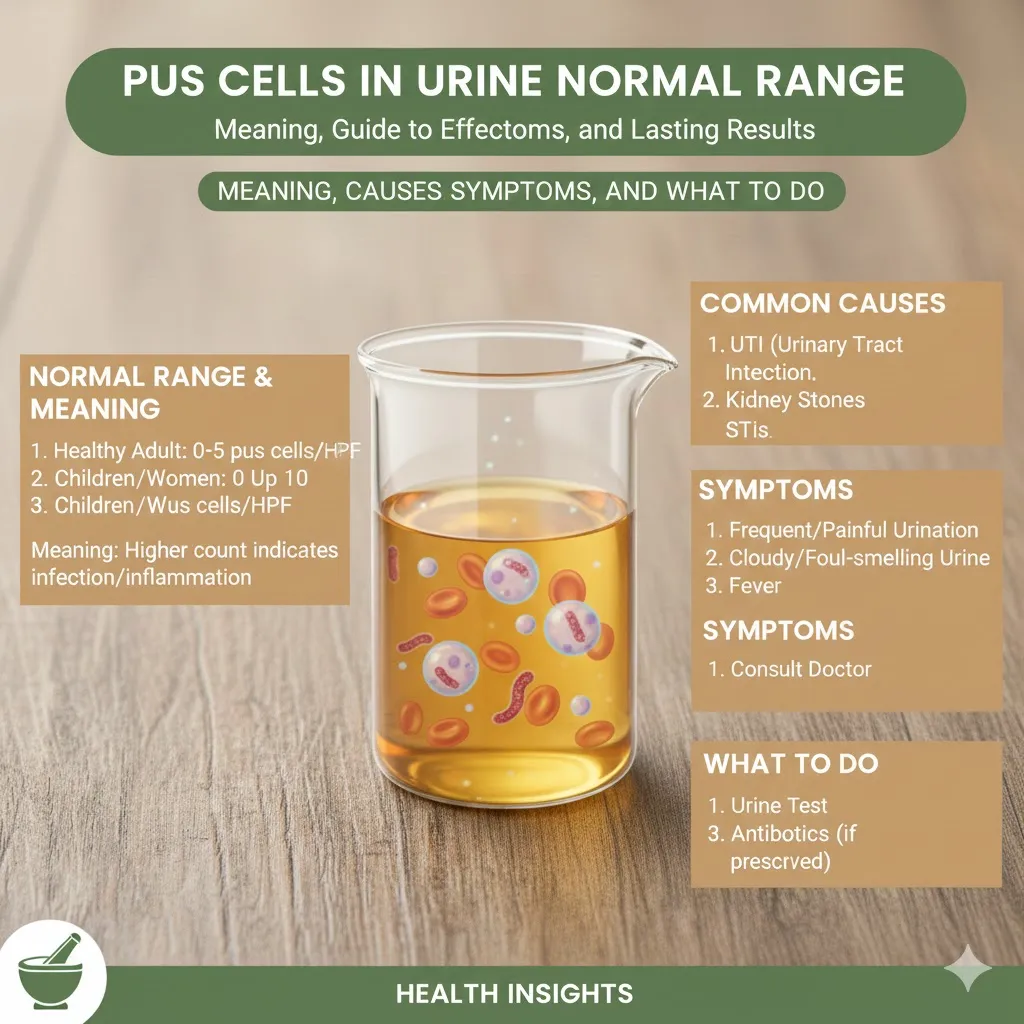
Pus Cells in Urine Normal Range Explained
The pus cells in urine normal range is typically:
- 0–5 pus cells per high power field (HPF) under a microscope
This range is considered normal and usually does not indicate any infection or disease. A count within this limit may occur due to minor contamination or temporary irritation and is often not clinically significant.
When pus cells exceed this normal range, further investigation may be required to identify the cause.
Why Is the Pus Cells in Urine Normal Range Important?
Understanding the pus cells in urine normal range is important because it helps:
- Detect urinary tract infections early
- Monitor kidney and bladder health
- Guide doctors in deciding further tests or treatments
- Differentiate between infection and non-infectious causes
A value above the normal range does not always mean a serious illness, but it should not be ignored.
What Does a High Pus Cell Count Indicate?
If the pus cell count is higher than the pus cells in urine normal range, it may indicate inflammation or infection. Common interpretations include:
- 6–10 pus cells/HPF: Mild infection or irritation
- 10–20 pus cells/HPF: Moderate infection
- More than 20 pus cells/HPF: Severe infection or inflammation
Doctors correlate these findings with symptoms and other test results before making a diagnosis.
Common Causes of Increased Pus Cells in Urine
When results exceed the pus cells in urine normal range, several conditions may be responsible.
1. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
UTIs are the most common cause of increased pus cells. Bacteria entering the urinary tract trigger an immune response, increasing white blood cells in urine.
2. Kidney Infection
Also known as pyelonephritis, this condition causes a significantly high pus cell count and often requires immediate medical treatment.
3. Bladder Inflammation
Inflammation of the bladder lining, known as cystitis, can elevate pus cells above the normal range.
4. Kidney Stones
Stones can irritate the urinary tract, causing inflammation and increased pus cells even without infection.
5. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Certain infections may cause pus cells to appear in urine samples, especially if symptoms involve the urethra.
Symptoms Associated with High Pus Cells in Urine
People with pus cells beyond the pus cells in urine normal range may experience:
- Burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Lower abdominal pain
- Fever or chills (in severe infections)
- Back or flank pain
Some individuals may have no symptoms, especially in mild cases.
Pus Cells in Urine Normal Range in Men, Women, and Children
The pus cells in urine normal range remains mostly the same across age and gender, but interpretation may vary slightly.
In Women
Women are more prone to UTIs due to shorter urethras. Minor elevations may occasionally occur due to contamination during sample collection.
In Men
Any pus cell count above the normal range may need closer evaluation, as UTIs are less common in men.
In Children
A high pus cell count in children should always be investigated to rule out infections or congenital issues.
How Is Pus Cell Count Measured?
A routine urine examination involves:
- Collecting a midstream urine sample
- Examining it under a microscope
- Counting pus cells per high power field
Accurate collection is essential to correctly assess the pus cells in urine normal range.
Difference Between Pus Cells and White Blood Cells
Pus cells are essentially white blood cells seen in urine microscopy. While blood tests also measure WBCs, pus cells specifically refer to WBCs present in urine, often indicating localized urinary tract inflammation.
Treatment for High Pus Cells in Urine
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and how much the count exceeds the pus cells in urine normal range.
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections
- Increased fluid intake: Helps flush bacteria
- Pain relievers: For discomfort
- Follow-up urine tests: To ensure recovery
Self-medication should be avoided, as improper treatment can worsen the condition.
Can Pus Cells Return to Normal Range Naturally?
In mild cases, especially when caused by dehydration or temporary irritation, pus cells may return to the pus cells in urine normal range with proper hydration and rest. However, persistent elevation usually requires medical treatment.
How to Maintain a Healthy Urinary System
To keep pus cells within the urine normal range:
- Drink plenty of water
- Maintain proper hygiene
- Avoid holding urine for long periods
- Urinate after sexual activity
- Follow a balanced diet
These habits help reduce infection risk and maintain urinary health.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a healthcare professional if:
- Pus cells exceed the normal range repeatedly
- Symptoms like pain, fever, or burning persist
- Blood is present in urine
- Symptoms worsen despite home care
Early medical intervention prevents complications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pus Cells in Urine Normal Range
Is 4–5 pus cells normal?
Yes, this falls within the pus cells in urine normal range.
Can stress increase pus cells?
Stress alone does not cause pus cells but may weaken immunity.
Is pus in urine always serious?
Not always. Mild elevations may resolve, but persistent findings require evaluation.
Final Thoughts on Pus Cells in Urine Normal Range
Understanding the pus cells in urine normal range helps reduce unnecessary anxiety and promotes timely medical care when needed. A count of 0–5 pus cells per HPF is considered normal and usually harmless. Values above this range may indicate infection or inflammation, but proper diagnosis depends on symptoms and additional tests.
Regular health check-ups, good hygiene, and prompt medical attention ensure urinary health and help keep pus cells within the normal range for long-term well-being.